Sun poisoning can be described, its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and treatment are all presented here if you wish to learn more about sun poisoning
Introduction:
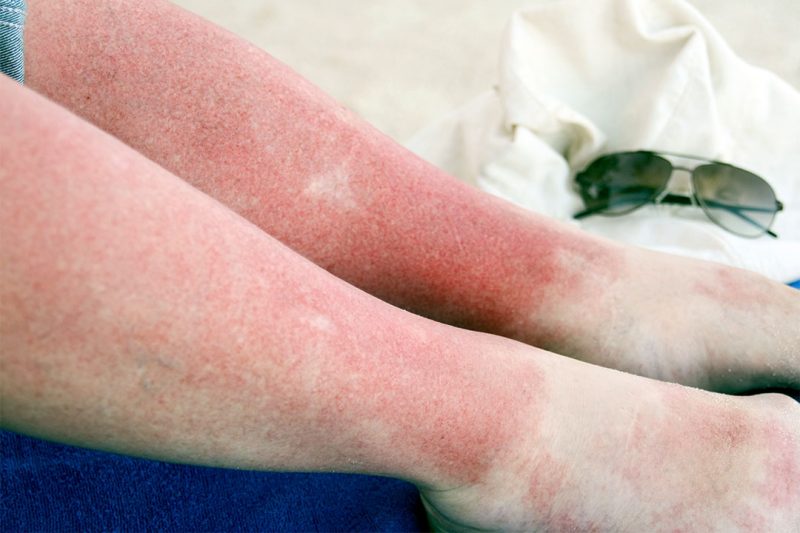
The condition known as sun poisoning is the result of excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UV), also known as severe sunburn or photodermatitis.
True poisoning is not what this condition is, but instead, a severe reaction characterized by blistering, fever, and dehydration. Those who are prone to sun sensitivity or who have compromised immune systems may be at risk for sun poisoning.
The purpose of this article is to provide a more in-depth examination of the causes, symptoms, and treatment options associated with sun poisoning.
What is sun Poisoning?
The condition of sun poisoning also called severe sunburn or photodermatitis occurs when the skin is overexposed to ultraviolet (UV) rays.
A reaction to excessive UV radiation is not true poisoning, but rather a severe reaction that may include blistering, fever, and even dehydration.
Individuals with compromised immune systems or those who are genetically predisposed to sun sensitivity are at greater risk of developing sun poisoning, which can be a serious and potentially life-threatening condition.
What Causes Sun Poisoning?
Sun poisoning is caused by excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources, such as tanning beds. Skin cancer can develop as a result of UV radiation damaging DNA in skin cells.
It is most likely that a person will suffer from sun poisoning during the summer months when the sun’s rays are at their strongest and when the Earth has the least amount of protection from UV rays.
A person can suffer sun poisoning due to two types of UV radiation: UVA and UVB radiation. Radiation with a longer wavelength, known as UVA radiation, can penetrate the skin more deeply, leading to premature aging as well as skin cancer.
Sunburn and skin cancer can be caused by ultraviolet B radiation, which is shorter-wavelength radiation.
Risk Factors for Sun Poisoning:
An individual may be at risk of developing sun poisoning due to several factors, including:
- Skin type: It is more likely that fair-skinned people, those with blond or red hair, and those with blue or green eyes will suffer from sun poisoning since they have less melanin, a pigment that protects from UV rays.
- Location: The sun’s rays are stronger at higher altitudes and closer to the equator, which puts people at greater risk of sun poisoning.
- Medications: Certain medications can increase an individual’s sensitivity to the sun, including antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and birth control pills.
- Health conditions: Skin can become more sensitive to the sun if it suffers from certain health conditions, such as lupus.
- Age: The thinner skin and greater sensitivity to UV radiation of children and older adults make them more vulnerable to sun poisoning.
Symptoms of Sun Poisoning:
There can be a wide range of symptoms associated with sun poisoning, including the following:
- Severe sunburn: A person suffering from sun poisoning may experience redness, swelling, and pain in their skin. It is also possible to experience blistering.
- Fever: During the process of fighting off the damaged skin cells caused by sun poisoning, the body may experience a fever.
- Dehydration: Dehydration may result from sun poisoning due to fluid loss from damaged skin. Thirst, dizziness, and a dry mouth may be symptoms of dehydration.
- Headache: Inflammation of blood vessels in the skin can result in a headache as a result of sun poisoning.
- Nausea: Inflammation of the digestive system may cause nausea in the case of sun poisoning. Inflammation of the digestive system may cause nausea in the case of sun poisoning.
- Fatigue: Several factors can contribute to fatigue caused by sun poisoning, including the body’s attempts to repair the damaged skin cells.
Treatment for Sun Poisoning:
There are several treatment options available for sun poisoning, depending on the severity of the symptoms.
It is possible to treat mild cases of sun poisoning at home with over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to alleviate the pain and inflammation associated with the condition.
Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids, such as water and sports drinks, is essential to replace the fluids lost as a result of the damage to the skin.
The more severe the case of sun poisoning, the more likely it is that medical treatment will be required. If severe dehydration or other complications occur, prescription medications, such as corticosteroids, may be required, in addition to hospitalization to treat dehydration.
A skin protection regimen should be implemented to prevent sun poisoning. The following steps can be taken to accomplish this:
- It is important to wear protective clothing, such as long sleeves, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses
- It is important to use sunscreen with a high SPF (Sun Protection Factor) and to apply it generously and frequently
- Avoiding direct sunlight between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., especially during peak UV hours
- The use of tanning beds, which emit high levels of ultraviolet radiation, should be avoided
The UV index should also be checked before spending time in the open air. Using the UV index, individuals can determine the level of protection they require based on the intensity of UV radiation.
Conclusion:
The condition of sun poisoning occurs when the body is overexposed to ultraviolet radiation. Individuals with compromised immune systems or those who are genetically predisposed to sun sensitivity may experience symptoms such as severe sunburn, fever, and dehydration as a result of this illness.
The best way to prevent sun poisoning is to wear protective clothing, use sunscreen, seek shade, and avoid tanning beds.
The importance of seeking medical attention as soon as possible if you are concerned that you may have sun poisoning is essential to prevent further complications.